Container Orchestration¶
For production, container-based services, you will often want to take advantage of a container orchestration engine to provide automated fail-over, load balancing, replication, and other high-level features. The most popular container orchestration engines are Kubernetes, Mesos, and Docker Swarm.
Docker Swarm¶
For resource-constrained environments like the NuvlaBox, we prefer to use Docker Swarm as a container orchestration engine. It is simpler to manage, more lightweight, and compatible with the standard Docker API.
Similar to the SlipStream components you have seen so far, Docker Swarm is available in the Nuvla App Store. Unlike the other examples however, this will be the first that involves multiple virtual machines. A Docker Swarm deployment consists of one master node and one or more worker nodes. Despite the additional complexity, a Docker Swarm cluster can be deployed as easily as the other examples.
Find the Docker Swarm tile in the App Store and click the Deploy
button to bring up the deployment dialog. You will see that the
dialog is more complex than before.
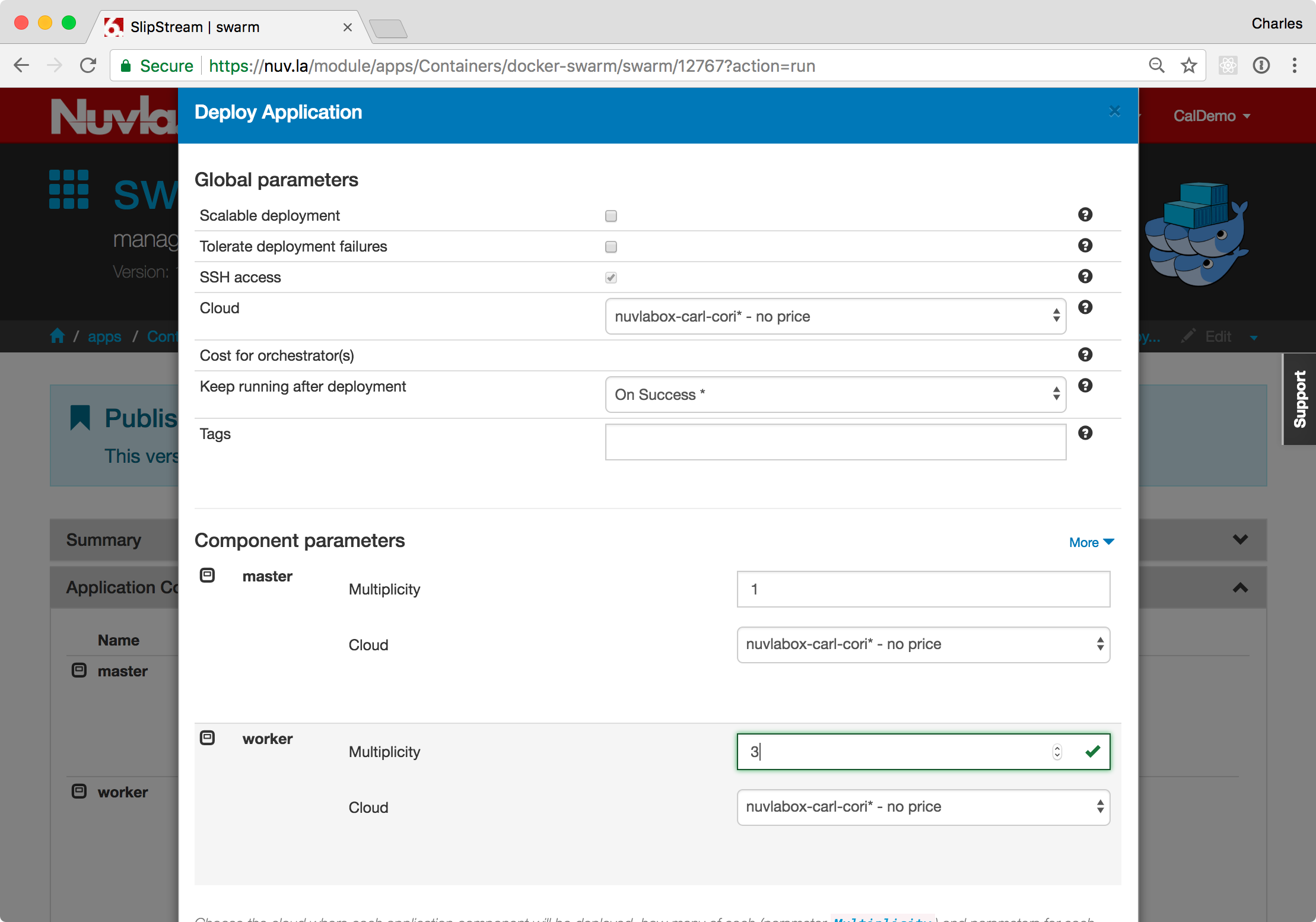
On the dialog, you see a general section, where you can choose the target infrastructure for all nodes. (You can also choose different infrastructures for different nodes, although we will not demonstrate that here.)
Then there is a section for each node of the deployment. Here there are two: “master” and “worker”. By default, you will have one master and one worker. You can increase the number of workers.
Once you have set the target infrastructure and the node
multiplicities, click the Deploy Application button to start the
deployment. As usual this will take you to the Dashboard where you
can follow the deployment process.
The deployment detail page will show the topology of the deployment and provide the input/output parameter values for all of the deployed nodes.
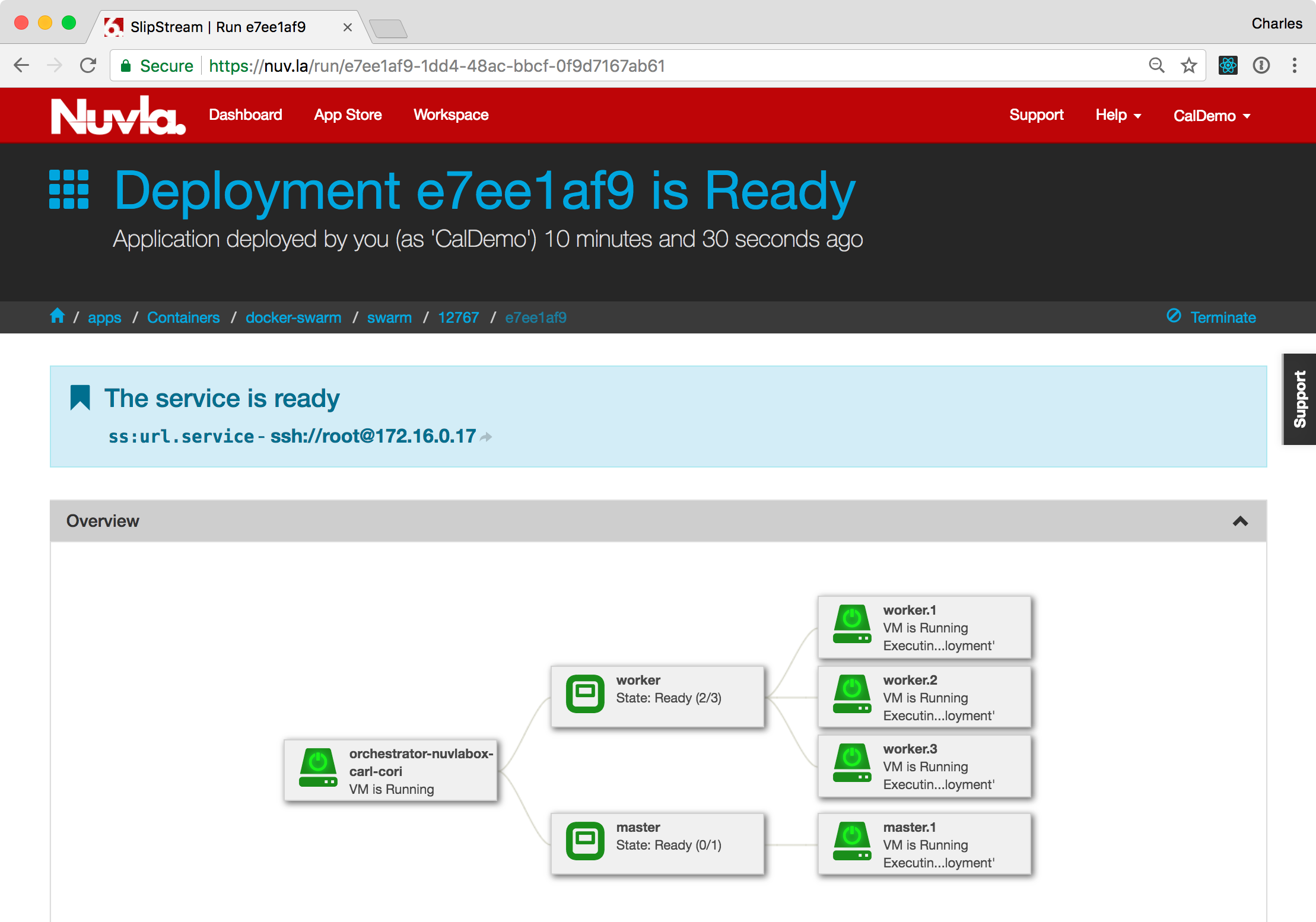
Note that the SlipStream application has handled the deployment of all of the virtual machines and coordinated the configuration of each node.
Replicated Service¶
The features provided by Docker Swarm for managing “services” are vast, so the SlipStream component does not try to provide a parameterized interface to the system. To manage services on the deployed Docker Swarm cluster, log into the master node via SSH. You can find the IP address on the deployment detail page.
When you have logged in, you can check that the number of nodes agrees with the number you requested:
$ docker node ls
ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION
cax3ifys3ixoogt0025k1o8bc * master1aab3929a-9167-4e73-8f65-29e33376b759 Ready Active Leader 18.03.1-ce
wwzmkb2q61o4r0ooe4wu3ug6q worker1aab3929a-9167-4e73-8f65-29e33376b759 Ready Active 18.03.1-ce
ic67gr0k1v0z5cin0fxvlcsd3 worker2aab3929a-9167-4e73-8f65-29e33376b759 Ready Active 18.03.1-ce
awd7cdf05i37xq4wmv4kubyb7 worker3aab3929a-9167-4e73-8f65-29e33376b759 Ready Active 18.03.1-ce
We asked for 1 master and 3 workers. They are all present and accounted for.
Now let’s use the Swarm to deploy a replicated nginx service. This command will run 3 replicas of nginx and make the service available on port 8080 from any node of the cluster:
$ docker service create --name nuvlacity_swarm \
--replicas 3 \
--publish published=8080,target=80 \
nginx
72ecrbhuy8p8o3h6jpmtn7v8c
overall progress: 3 out of 3 tasks
1/3: running [==================================================>]
2/3: running [==================================================>]
3/3: running [==================================================>]
verify: Service converged
You can then check that the service is running with the correct configuration:
$ docker service ls
ID NAME MODE REPLICAS IMAGE PORTS
72ecrbhuy8p8 nuvlacity_swarm replicated 3/3 nginx:latest *:8080->80/tcp
The nginx server should respond from any node within the cluster. You can get the IP address of the nodes through Nuvla or via Docker:
$ docker node inspect -f '{{ .Status.Addr }}' wwzmkb2q61o4r0ooe4wu3ug6q
159.100.241.48
Using curl to get the page content:
swarm-master# curl 159.100.241.48:8080
<!DOCTYPE html>
...
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
...
</html>
You can verify that this works from all nodes of the Docker Swarm cluster.
Summary¶
With Nuvla, you can deploy a full container orchestration engine easily, allowing you to take advantage of the replication, load balancing, and other features. Tighter integration of SlipStream with Docker Swarm is in the development roadmap.